US Quiz of the Month – August 2021
CASE REPORT
A 62 years-old female patient with a personal medical history of a JAK2 mutation-negative essential thrombocythemia under hydroxyurea was referred for an endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) due to a perihepatic hypodense ovoid lesion on abdominal computed tomography. The lesion measured 20×16 mm, and was mildly enhanced in arterial phase and moderately enhanced in portal phase. Apart from a mild abdominal pain in the previous months, the patient did not report any other symptoms. She denied past abdominal trauma or surgeries. Laboratory studies were unremarkable. The EUS revealed in the periportal region, a nodular lesion with 18x14mm, isoechogenic in relation to the liver parenchyma, with distinct margins and well-demarcated from the surrounding organs (Fig. 1). No enlarged hilar lymph nodes or left liver masses were recognized.

Figure 1. EUS (transduodenal view): nodular lesion, isoechogenic in relation to the liver parenchyma, well-demarcated from the surrounding organs in the periportal region.
Tissue sampling was obtained through fine needle biopsy (FNB), 3 passages, using an AcquireTM 22G needle (Boston Scientific) (Fig. 2).

Figure 2. EUS-guided FNB (22G, AcquireTM, Boston Scientific) of the mass was performed.
Histopathological analysis (Fig. 3A) identified a mesenchymal tumor with spindle cells arranged in bundles and palisades with no nuclear atypia. Immunohistochemical staining (Fig. 3B) was diffusely positive for S-100 protein, and with no expression for DOG1, CD117, alpha-actin, smooth muscle actin, desmin and CD34.
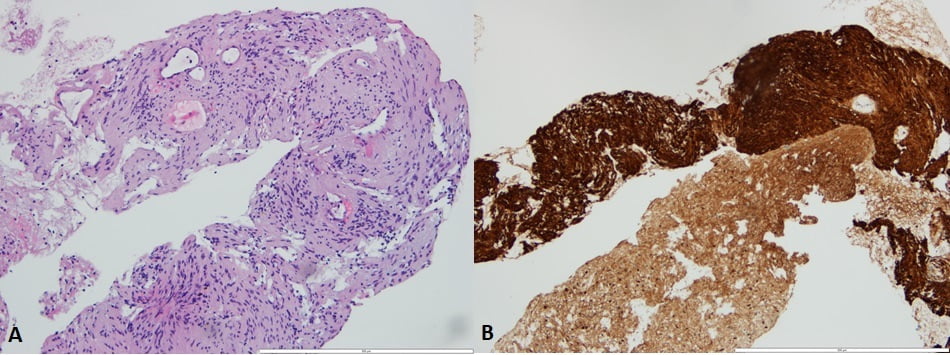
Figure 3. A – Histopathological analysis revealing a mesenchymal tumor with spindle cells arranged in bundles and palisades with no nuclear atypia; B – Immunohistochemical staining positive for S-100 protein, and negative for DOG1, CD117, alpha-actin, smooth muscle actin, desmin and CD34.
WHAT IS THE MOST LIKELY DIAGNOSIS?
DISCUSSION
The histopathological analysis was compatible with a schwannoma.
A schwannoma is a tumor that arises from Schwann cells, which form the inner portion of the peripheral nerve sheath(1). Intraperitoneal schwannomas are relatively uncommon, and porta hepatic schwannomas are even rarer, with very few (<20) cases described in the literature(1). Tumors in this region can be associated to symptoms by compressing adjacent structures, although 40% of patients are asymptomatic. As imaging characteristics are nonspecific, patients are usually misdiagnosed, unless a biopsy is performed. It is essential to combine histological examination with immunohistochemical staining, which typically shows positivity for S-100 protein. Few gastrointestinal stromal tumors are also positive for S-100 protein, although in these cases positivity for either CD-34 or CD117 is also present(2). The main treatment of porta hepatic schwannomas is complete excision with free margins and most cases do not relapse, making the overall prognosis very good(1). Malignant transformation of these tumors is very rare(3).
In a previous literature review evaluating 15 cases of a porta hepatic schwannoma, fine needle aspiration (FNA) showed inconsistent final pathologic results, advocating the need of biopsy material. This case emphasizes the importance of EUS-FNB for the diagnosis of a mesenchymal tumor in which immunohistochemistry was essential to differentiate it from other similar entities.
REFERENCES
- Yin S-y, Zhai Z-l, Ren K-w, Yang Y-c, Wan D-l, Liu X-y, et al. Porta hepatic schwannoma: case report and a 30-year review of the literature yielding 15 cases. World J Surg Oncol. 2016;14:103.
- Miettinen M, Lasota J. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors: review on morphology, molecular pathology, prognosis, and differential diagnosis. Archives of pathology & laboratory medicine. 2006;130(10):1466-78.
- Ducatman BS, Scheithauer BW, Piepgras DG, Reiman HM, Ilstrup DM. Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors. A clinicopathologic study of 120 cases. Cancer. 1986;57(10):2006-21.
AUTHORS
Gomes C1, Moutinho-Ribeiro P2, Magalhães J3, Macedo G2.
- Gastroenterology Department, Centro Hospitalar Vila Nova de Gaia/Espinho, Portugal.
- Gastroenterology Department, Centro Hospitalar Universitário de São João, Portugal.
- Pathology Department, Centro Hospitalar Universitário de São João, Portugal.


